RSA Encryption and Decryption with Python’s PyCryptodome Library
-
 Miyoko Shimura
Miyoko Shimura - 20 Jun, 2024

In this guide, I’ll show you how to encrypt and decrypt messages using RSA public key cryptography in Python, utilizing the PyCryptodome library.
RSA allows for secure data transmission using a key pair consisting of a public key and a private key. Understanding RSA is not only vital for data security but also offers valuable insights into the principles of cryptography.
Overview of RSA Algorithm
RSA is a public-key cryptography algorithm developed 1970’s by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman at MIT. RSA was publicly described in 1977 and the algorithm patented. The patent expired in 2000 allowing free public use.
RSA is an asymmetric cryptography algorithm which enables secure data transmission using a public and private key pair. RSA was initially slow compared to symmetric ciphers but improved over time.
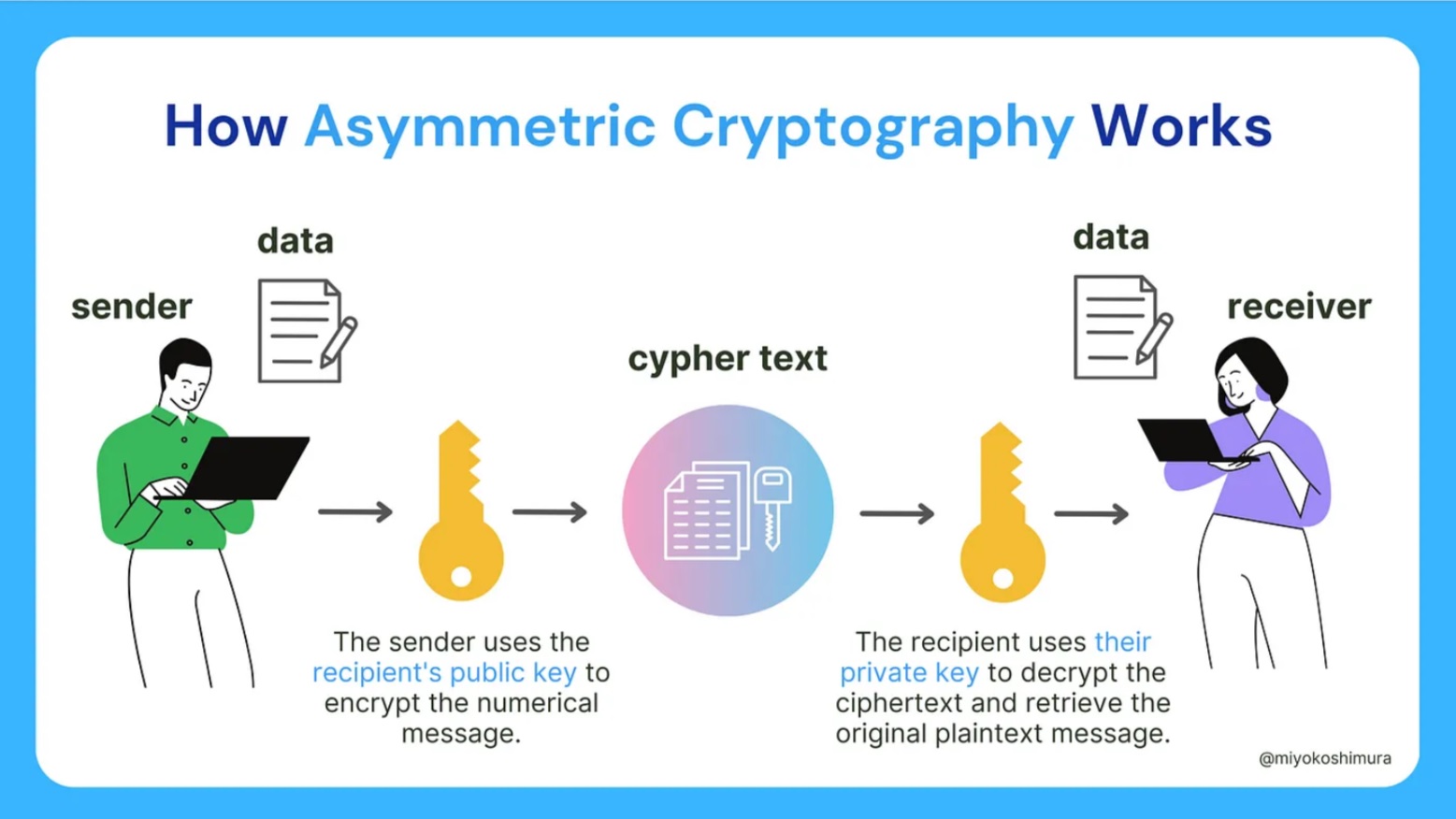
How Asymmetric Cryptography Works
RSA’s security is rooted in the difficulty of factoring a large number 𝑛, which is the product of two large prime numbers. This problem is computationally hard for sufficiently large values of 𝑛, making RSA encryption secure when using appropriately sized keys, typically 2048 bits or larger.
RSA Use Cases
- Secure Communication: TLS/SSL encryption for internet security.
- Digital Signatures: Verifies document authenticity through digital signatures.
- Secure Email: Encrypts and verifies emails for confidentiality.
- File Transfer Security: Ensures secure and verified file transfers.
- SSL/TLS Certificates: Integral for securing websites and online transactions.
- VPN Security: Establishes secure communication in virtual private networks.
- Authentication: Used in smart cards for secure user authentication.
Setting Up Python Environment with “PyCryptodome”
First, we set up a Python environment with the necessary library for cryptographic operations and use the “PyCryptodome” library built upon the now-deprecated “PyCrypto.”
Step 1: Installing libraries in Python
The PyCryptodome library serves as a comprehensive Python package of low-level cryptographic primitives. To install it, run the following commands.
# Step 1: Install PyCryptodome package
!pip install pycryptodome
# Import necessary modules from PyCryptodome
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Cipher import PKCS1_OAEP
# This module converts binary data to hexadecimal
from binascii import hexlify
Step 2: Generating RSA Key Pair
After setting up your Python environment, generate an RSA key pair. In this example, we’ll use a 1024-bit key.
# Step 2: Generate new RSA key
# Create an RSA key pair with a key size of 1024 bits
key = RSA.generate(1024)
# Set the private_key variable to the generated key
private_key = key
# Derive the public key from the generated key
public_key = key.publickey()
Step 3: Encrypting Data with Public Key
In this example, we’ll encrypt the message “Hello, this is a message to be encrypted.”
# Step3: Encrypt using public key
# Create a PKCS1_OAEP cipher object with the public key for encryption
data_to_encrypt = b"Hello, this is a message to be encrypted."
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(public_key)
# Encrypt the provided data using the public key
encrypted = cipher_rsa.encrypt(data_to_encrypt)
# Convert binary data to hexadecimal for display using hexlify
print("Encrypted:", hexlify(encrypted))
Step 4 : Decrypting Data with Private Key
# Step4: Decrypt using private key
# Create a PKCS1_OAEP cipher object with the private key for decryption
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(private_key)
decrypted = cipher_rsa.decrypt(encrypted)
# Display the decrypted result as a UTF-8 encoded string
print("Decrypted:", decrypted.decode("utf-8"))v
Step 5: Result
Encrypted: b’3278c4093d20026311c0d3e70305b004ffec84b5d6636b2a4991e196f0065c946083d15f1c304f37b48c8b0ea7fe56fe3327150af555e8e903a13c7c797545d9ddd358c2d581f9070a98ad5bd8a4a6a725103346b53ba927f74e6730a62c38a4cb566f04c428a30a82d983f55358b4e201db9ce78741bf2de0d575e5ba248fc8'
Decrypted: Hello, this is a message to be encrypted.
Full Python Code
# Step1: Install PyCryptodome package
!pip install pycryptodome
# Import necessary modules from PyCryptodome
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Cipher import PKCS1_OAEP
# This module converts binary data to hexadecimal
from binascii import hexlify
# Step2: Generate new RSA key
# Create an RSA key pair with a key size of 1024 bits
key = RSA.generate(1024)
# Set the private_key variable to the generated key
private_key = key
# Derive the public key from the generated key
public_key = key.publickey()
# Step3: Encrypt using public key
# Create a PKCS1_OAEP cipher object with the public key for encryption
data_to_encrypt = b"Hello, this is a message to be encrypted."
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(public_key)
# Encrypt the provided data using the public key
encrypted = cipher_rsa.encrypt(data_to_encrypt)
# Convert binary data to hexadecimal for display using hexlify
print("Encrypted:", hexlify(encrypted))
# Step4: Decrypt using private key
# Create a PKCS1_OAEP cipher object with the private key for decryption
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(private_key)
decrypted = cipher_rsa.decrypt(encrypted)
# Display the decrypted result as a UTF-8 encoded string
print("Decrypted:", decrypted.decode("utf-8"))
Conclusion
Utilizing Python’s “PyCryptodome” library provides practical insights into the inner workings of cryptographic algorithms. Yet, it’s vital to always handle private keys with care to ensure the security of your encrypted data. Hope you enjoyed an enigmatic journey into the cryptography!


